Fats

What is fat?
We hear a lot about it – saturated fat, heart-healthy fats, Omega 3s, low-fat diet, high-fat diet, and more. But, do we need it? Yes!
Fat is one of the three types of nutrients that give us calories (energy). The other two are proteins and carbohydrates. We need all three to survive.
Your body needs fat to:
- Allow for long-term energy storage
- Give you energy and keep you feeling full
- Help absorb Vitamins A, E, D and K
- Help keep your body at the right temperature
- Support many cell functions
Types of fats
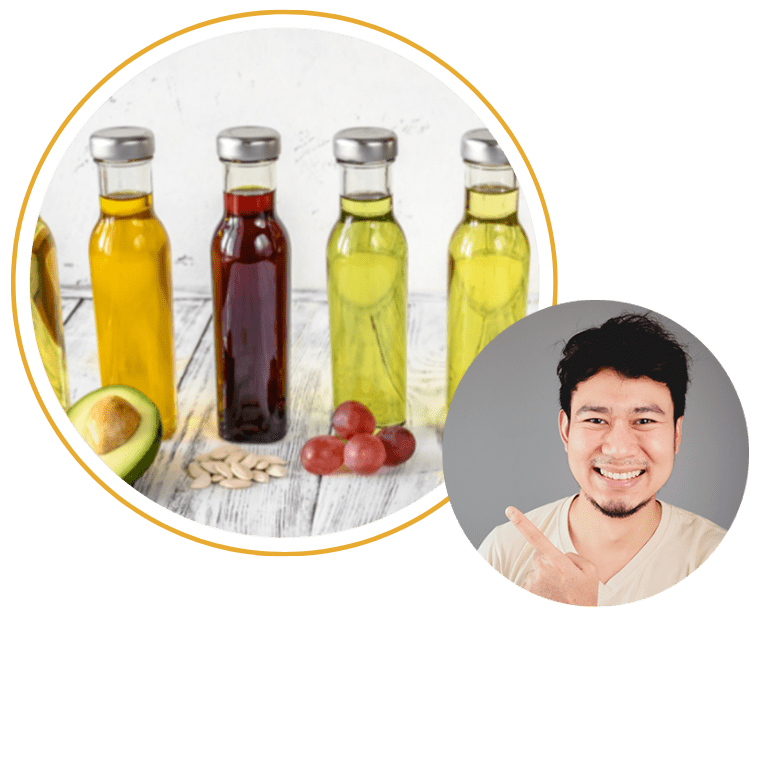
The most common forms of fat found in food are:
Unsaturated fat
This fat is liquid at room temperature and has heart-healthy properties. There are 2 types of unsaturated fats: monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats (including: omega 3). Both are considered heart-healthy. Unsaturated fats raise your HDL cholesterol, your ‘good’ or ‘Happy’ cholesterol.
Examples of foods with unsaturated fats are:

Be aware:
Some people with kidney disease need to limit how much potassium they eat. Nuts and avocados are higher potassium foods. Ask your dietitian how to fit these heart healthy foods into your meals!

Olive oil (monounsaturated)

Canola oil (polyunsaturated)

Salmon

Nuts

Avocados
Saturated fat
Saturated fat is solid at room temperature, like butter or the marbling in a steak. Eat these types of fats in small amounts because they cause your LDL ‘bad’ or ‘Lousy’ type of cholesterol to increase, which can lead to heart disease.
Examples of foods with saturated fats are:

Lard

Solid vegetable shortening

Butter

Coconut oil

Animal fat – (the marbling on a steak, bacon, chicken skin)

Trans fat
Trans fats are man-made fats and are ‘hidden’ in many processed foods. Although trans fats keep our food fresher longer, they lower your HDL (Happy cholesterol) and raise your LDL (Lousy cholesterol), which can lead to heart disease.
Trans fats are required to be included on the nutrition label. You can find trans fats listed as ‘partially hydrogenated’ fat or oil on a nutrition label.
In June 2018, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) required food companies to start removing trans fats from processed foods. They expect trans fats to be completely removed by all processed foods by 2023.
Your support goes further with AKF
Your donation allows AKF to support people wherever they are in their fight against kidney disease – from prevention through transplant. For more than 50 years, we have fought on all fronts for millions of people impacted by kidney disease.
Donate today to support our work